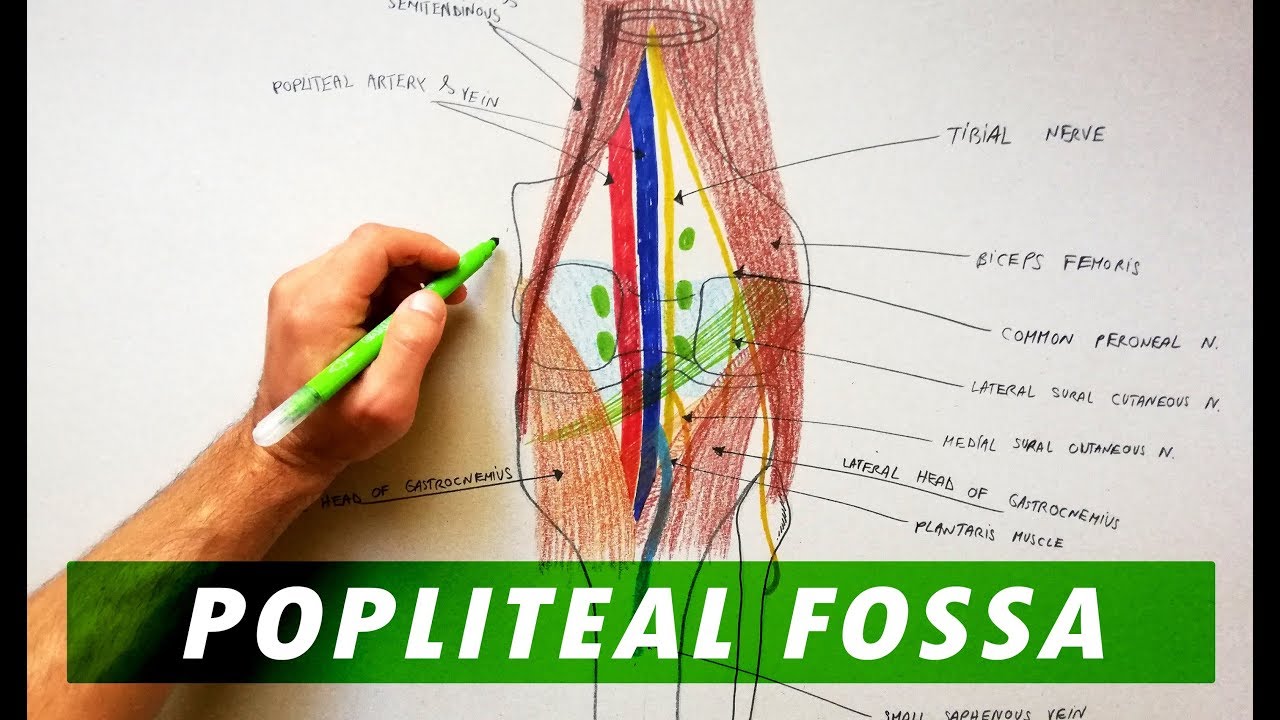
Popliteal fossa Mnemonic PeN TiN VAN From lateral to medial Peroneal Nerve;2 The popliteal artery itself lies deepest of all in the fossa 3 Fat 4 Popliteal lymph Popliteal pulse is the toughest (difficult) pulse to feel amongst all the peripheral pulses Popliteal aneurysm The popliteal artery is more prone to an aneurysm than any other artery in the body Clinically, the popliteal aneurysm mostly presents as a pulsatile midline swelling in the popliteal fossa Baker's cyst

Popliteal Fossa Its Boundaries Contents And Clinical Correlates Kyrmed
Popliteal fossa artery vein nerve
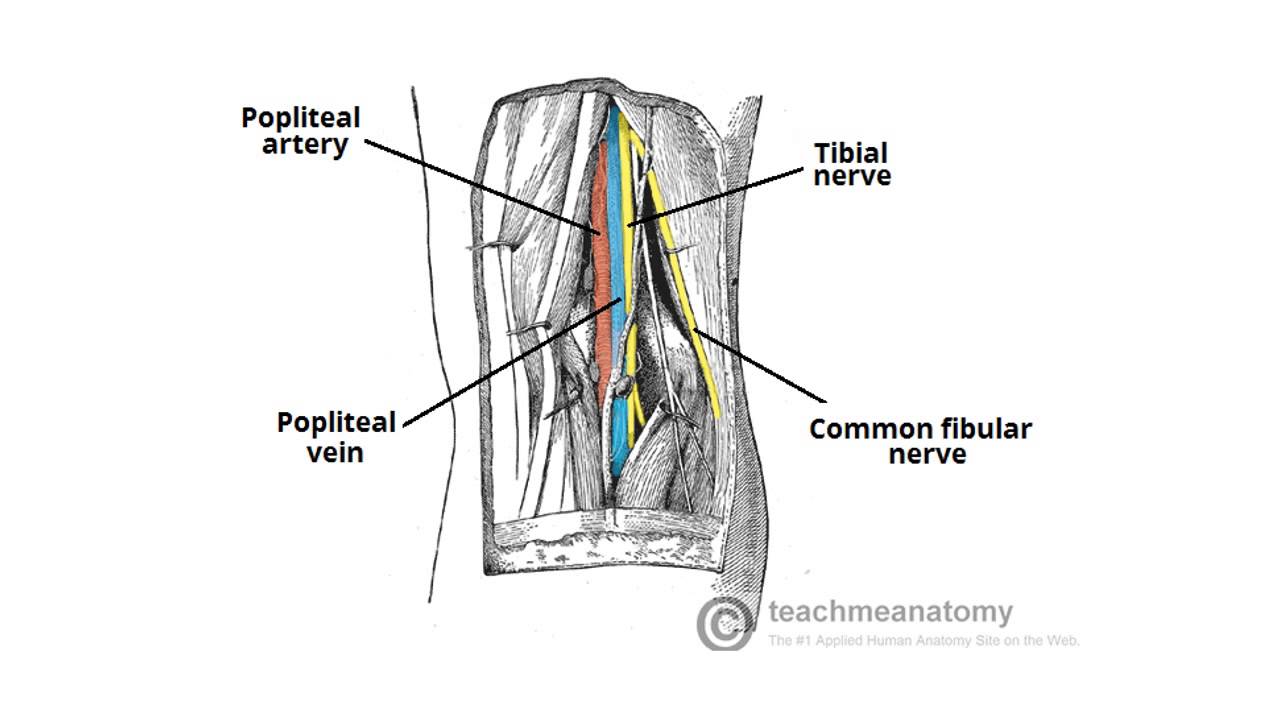
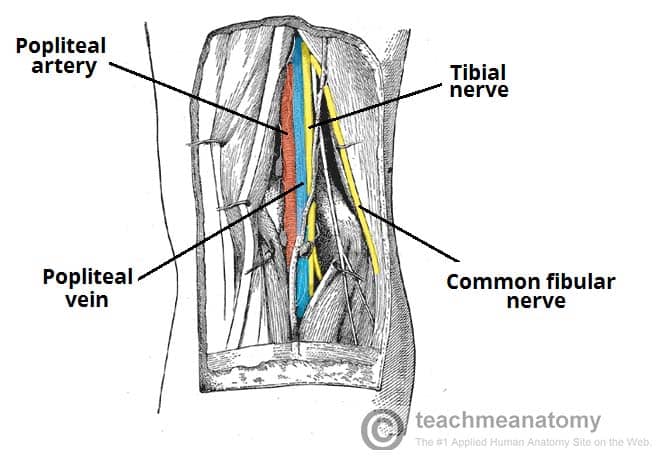
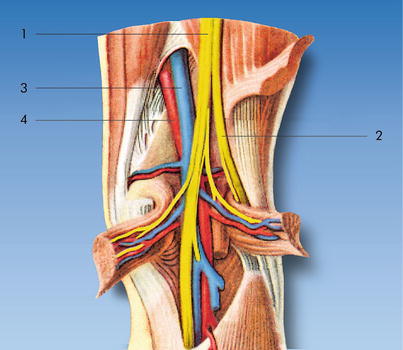
Popliteal fossa artery vein nerve-In anatomy, a hollow or depressed area amygdaloid fossa the depression in which the tonsil is lodged cerebral fossa any of the depressions on the floor of the cranial cavity condylar fossa ( condyloid fossa ) either of two pits on the lateral portion of the occipital The tibial nerve is first lateral to the popliteal vessels and then crosses superficially to these vessels to lie on their medial side PoplitealV Tibial N PoplitealA Common Fibular N 8 1 The popliteal vein lies immediately superficial to the artery;




Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora
The course of the popliteal artery and vein can be traced through the fossa to the passage of the vessels deep to soleus They are accompanied by the tibial nerve, with the lateral head of the gastrocnemius removed several muscular branches of the tibial nerve are visible in the fossa (as is the medial sural cutaneous nerve and the distalmost•Describe the applied anatomy of the popliteal fossa Preface •Important transition area •Between thigh and leg •Passes structure between two Location •Diamond shaped space Artery, vein, nerve •Middle part (superficial to deep) Nerve, vein, artery •Lower part (medial to lateral) Nerve, vein, artery Popliteal vessels The sciatic nerve was found to be entrapped before its division to the tibial and common peroneal nerves from the terminal branch of the small saphenous vein (SSV) into the popliteal vein (PV) The terminal section of SSV was subsequently ligated and resected to relieve the pressure on the sciatic nerve
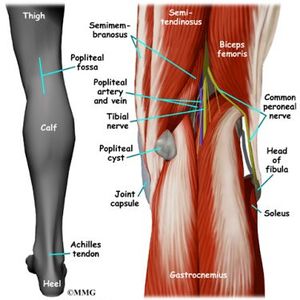
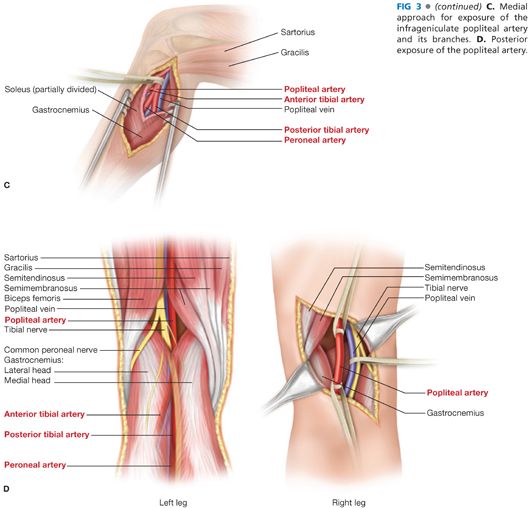
The lower extremity consists of the hip, thigh, knee, and popliteal fossa, as well as the leg (crus), ankle, and foot The leg (crus) extends from the knee to the ankle and contains the tibia and fibula The tarsal bones include the calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular bones , and the medial, middle, and lateral cuneiform bones The medial cutaneous sural nerve is located deep to the fascia and is the first nerve encountered in the posterior approach It, like the tibial and peroneal nerves, is best retracted laterally in exposing the popliteal artery • The tibial nerve is lateral and superficial within the popliteal fossa It is large and easily identified The popliteal fossa is a diamondshaped intermuscular space situated at the back of the knee The fossa is most prominent when the knee joint is flexed It contains the popliteal vessels, the small saphenous vein, the common peroneal and tibial nerves, the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, the genicular branch of the obturator nerve
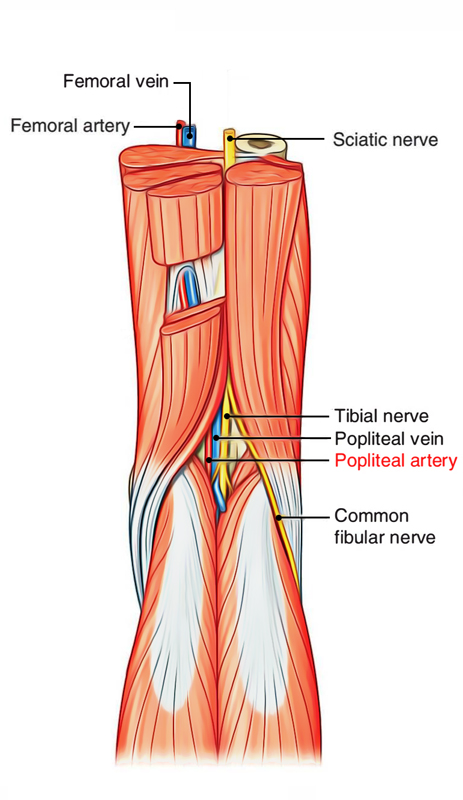
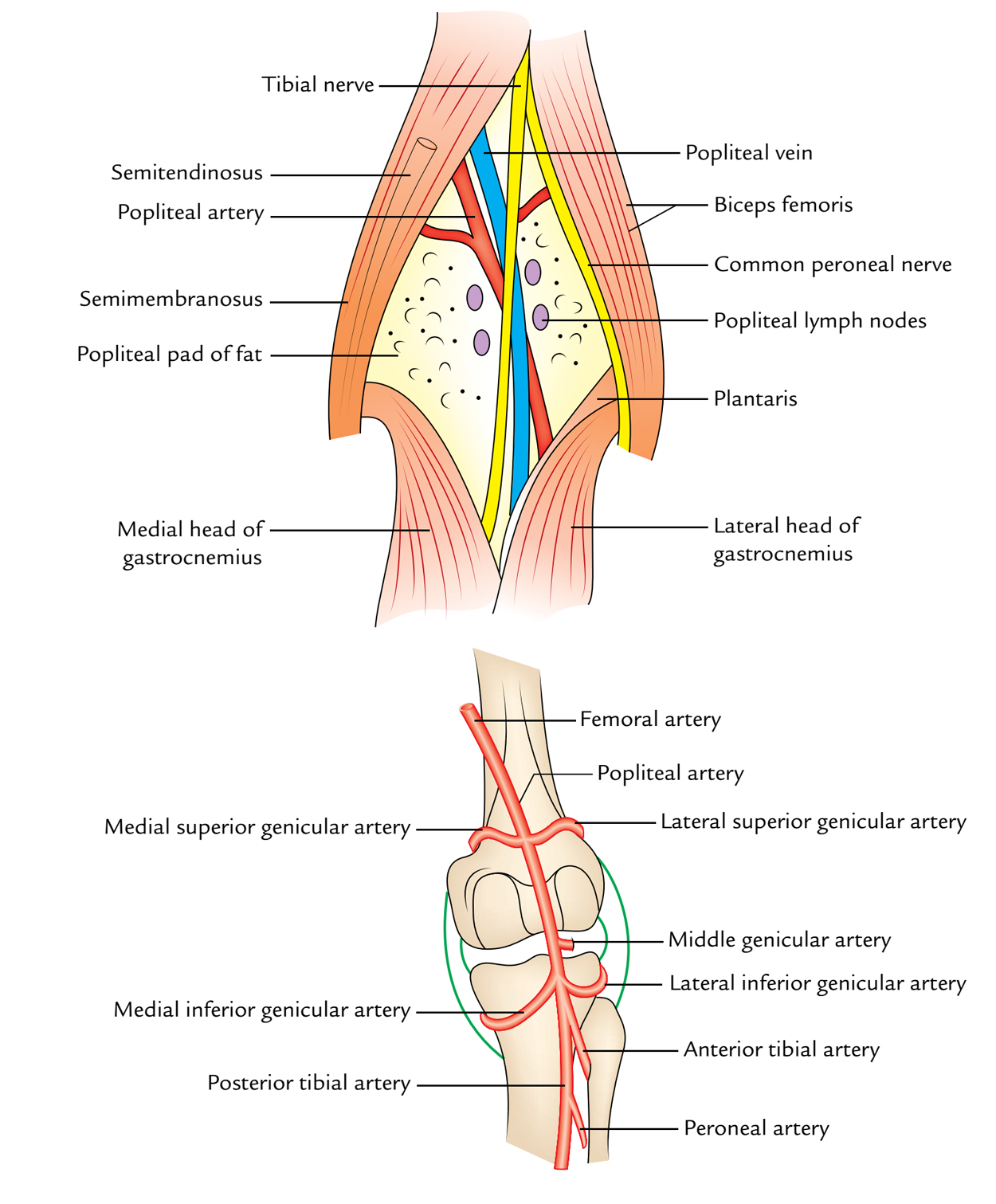
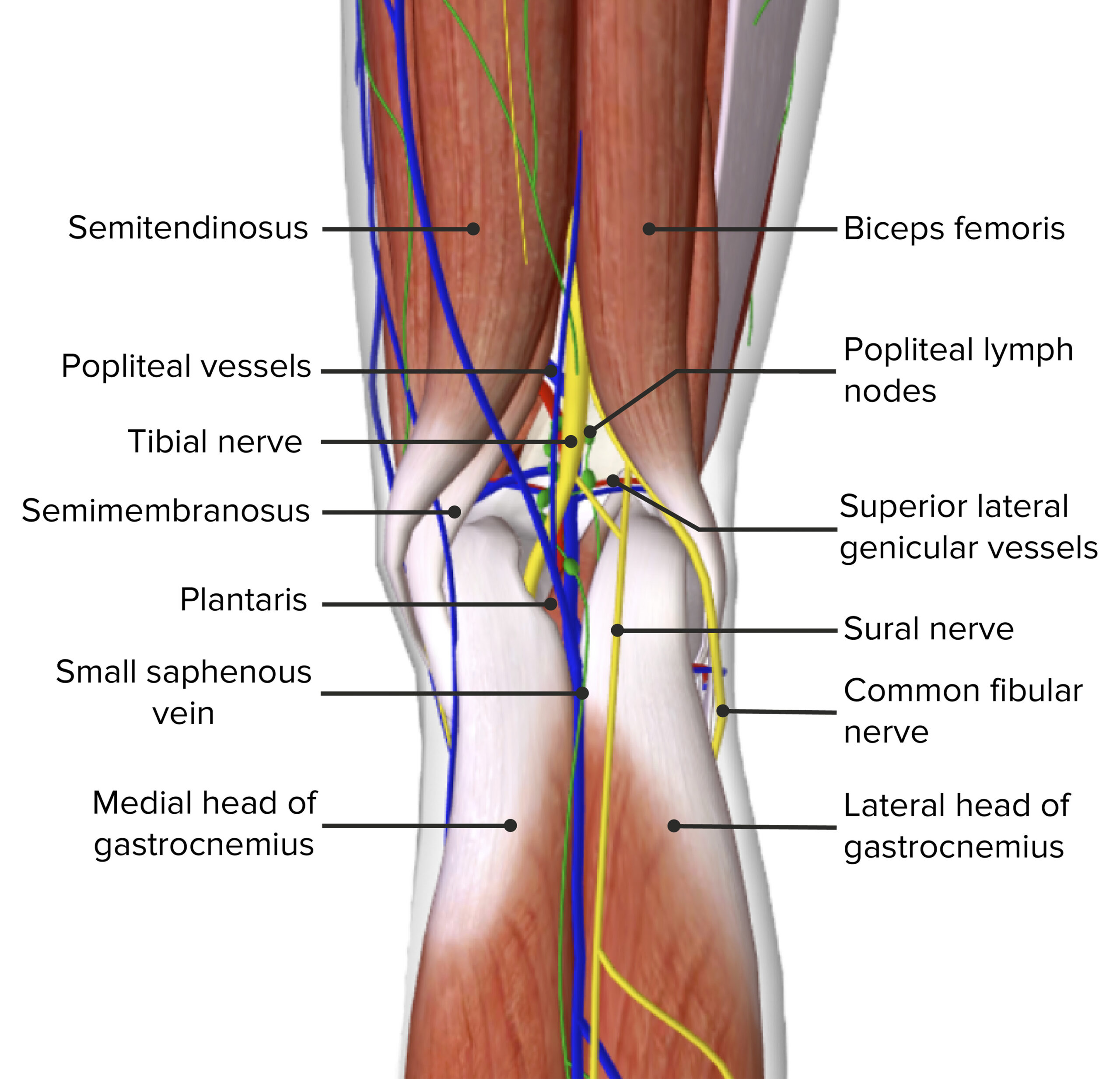
Femoral Vein Femoral Artery Femoral Nerve What are the boundaries of the femoral canal?It goes vertically downward from superior angle to inferior angle of popliteal fossa It crosses popliteal artery from lateral to medial side and lies superficial to popliteal artery in popliteal fossa Popliteal vein lies in between artery and nerve In lower part of popliteal fossa covered by two heads of gastrocnemius Popliteal fossa Boundaries The superomedial aspect of the popliteal fossa is bounded by the semimembranosus and the semitendinosus Nerves The popliteal fossa is 25 cm wide and mainly consists of fat tissue There are many important neurovascular Blood vessels Blood vessels are located deep




Poplitealfossa Explore Facebook
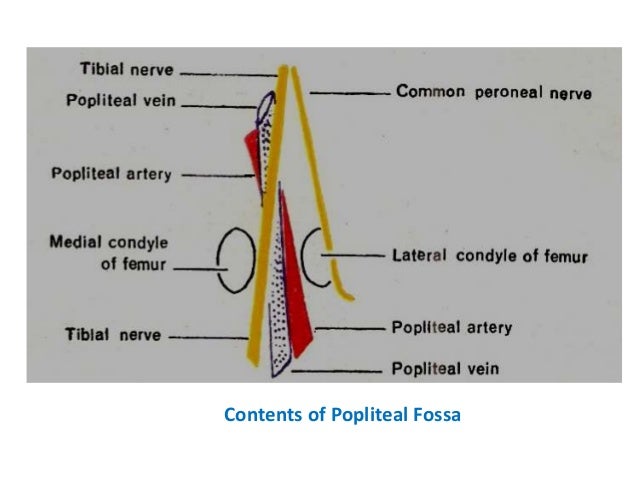



2 Popliteal Fossa
The popliteal vessels and branches are found directly beneath the fibular periosteum, with the artery usually located anterior to the posterior tibial nerve and the popliteal vein Extending the dissection distally allows exposure and control of distal popliteal artery, as well as the origins of the anterior tibial and the tibioperoneal trunk Sonoanatomy of the Sciatic Nerve in the Popliteal Fossa The sciatic nerve is imaged by placing the ultrasound probe in a transverse orientation on the posterior aspect of the patient's leg, in the popliteal fossa (Sonoanatomy Figs 624 and 625 )The popliteal vessels and the tibial nerve are arranged one over the other Structures arranged from deep to superficial are;
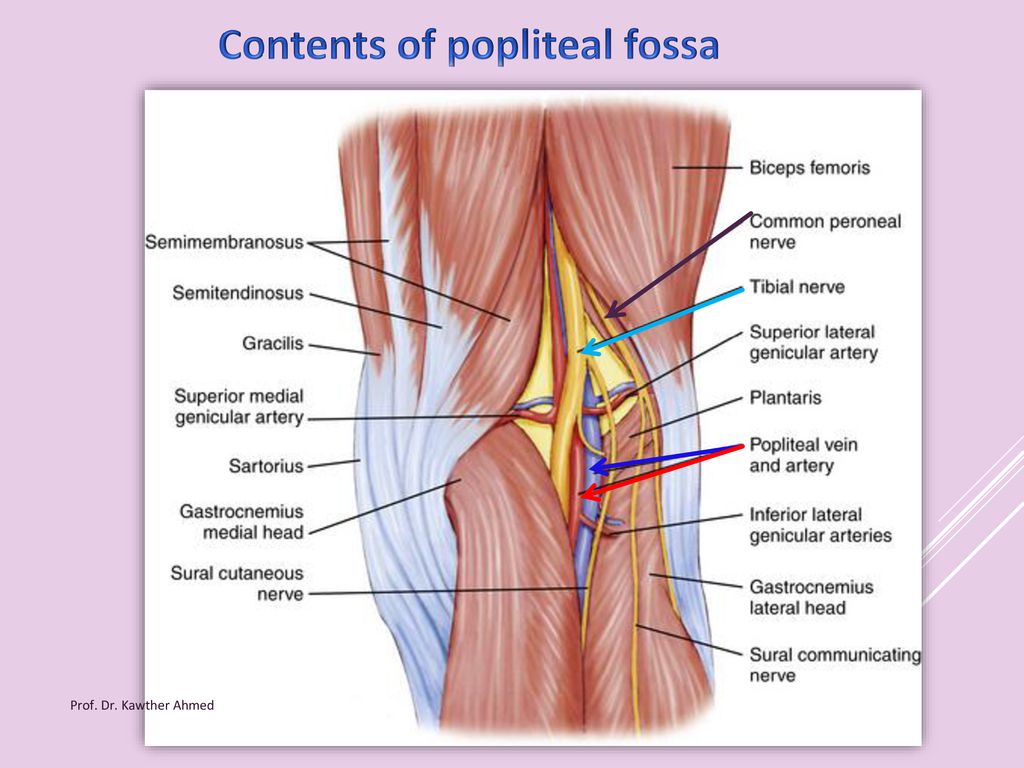



Popliteal Fossa By Prof Dr Kawther Ahmed Prof Dr Kawther Ahmed Ppt Download




Figure 1 From The Small Saphenous Vein And Other Neglected Veins Of The Popliteal Fossa A Review Semantic Scholar
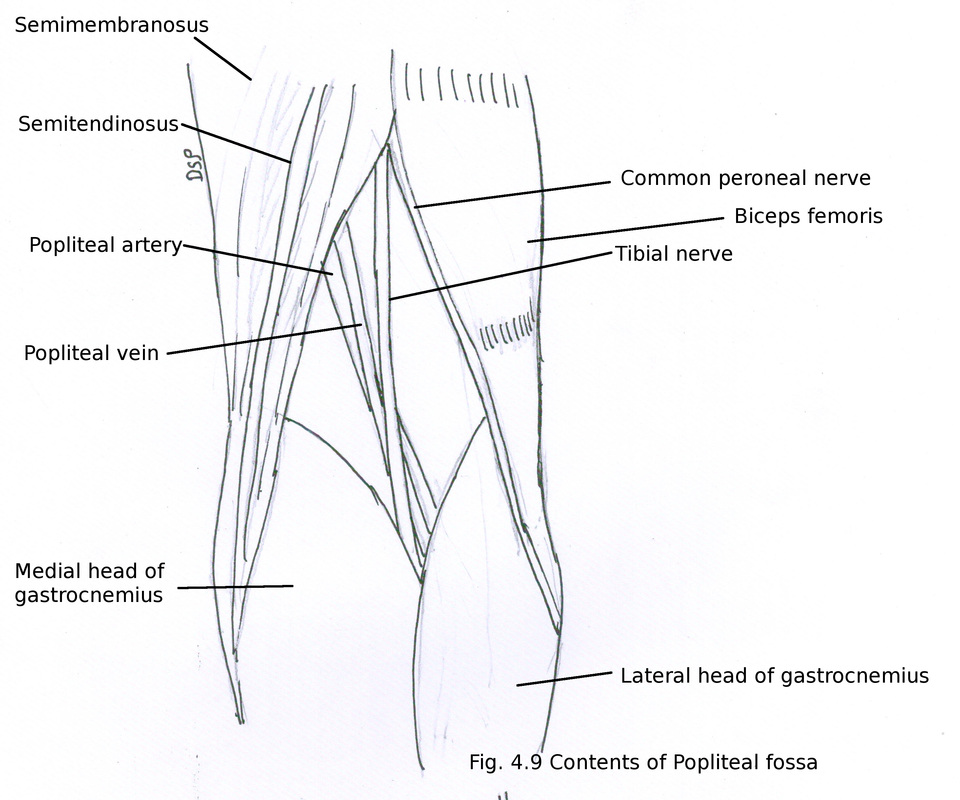
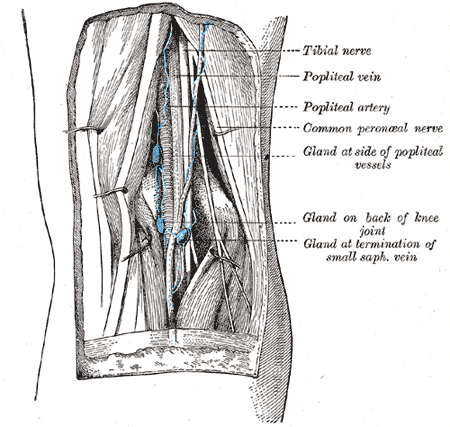
Median cubital vein (preferred site of venipuncture;(Which divides into Tibial and Common Fibular nerves at the apex) Popliteal Vein (Becomes femoral vein at adductor hiatus) Popliteal Artery Sets with similar terms Nerve information Contents of Popliteal Fossa The popliteal artery and popliteal vein The small saphenous vein, The common peroneal and tibial nerves The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, The genicular branch of the obturator nerve Connective tissue, and lymph nodes 7



1




Popliteal Artery Location Entrapment Popliteal Artery Aneurysm
The popliteal fossa contains the popliteal artery, the popliteal vein, the tibial nerve, and the common fibular nerve (Figure 2) The popliteal artery is the deepest of the structures in the fossa and descends through the region from the upper medial side—The popliteal fossa contains the popliteal vessels, the tibial and the common peroneal nerves, the termination of the small saphenous vein, the lower part of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, the articular branch from the obturator nerve, aDissection of 19 lower limbs, including six with intravascular injection of latex, allowed gross and microscopic measurements to be made of the blood supply of the common peroneal nerve in the popliteal fossa This showed that a long segment of the nerve in the vicinity of the fibular neck contained only a few intraneural vessels of fine calibre
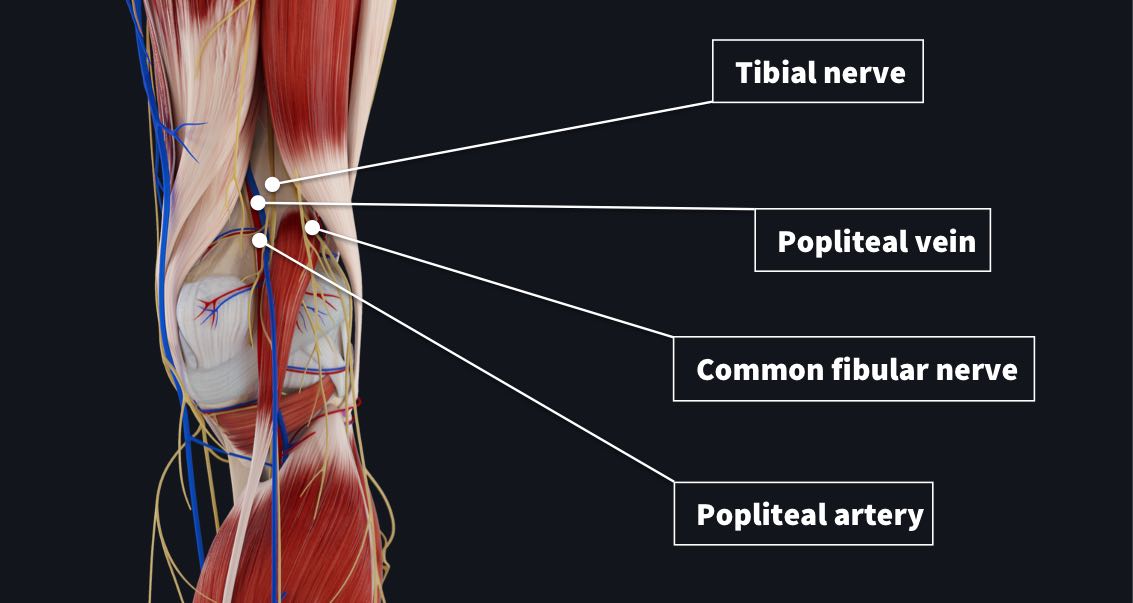



The Popliteal Fossa Complete Anatomy




Thigh Knee And Popliteal Fossa Knowledge Amboss
It is important to note that the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa is lateral and superficial to the popliteal artery and vein, and it is contained in its own tissue (epineural) sheath rather than in a common neurovascular tissue sheath This anatomic characteristic explains the relatively low risk of systemic toxicity and vascular puncturesVein (Popliteal vein) Artery (Popliteal artery) Nerve (Genicular branch of obturator nerve – descends upon popliteal artery) Intercostal space Superior to inferior along the inferior Subsequent MRI confirmed a 3 cm pedunculated osteochondroma on the posteromedial aspect of the left femur It passed directly through the neurovascular bundle (popliteal vein medially, artery and tibial nerve laterally) with no evidence of malignant transformation or soft tissue invasion
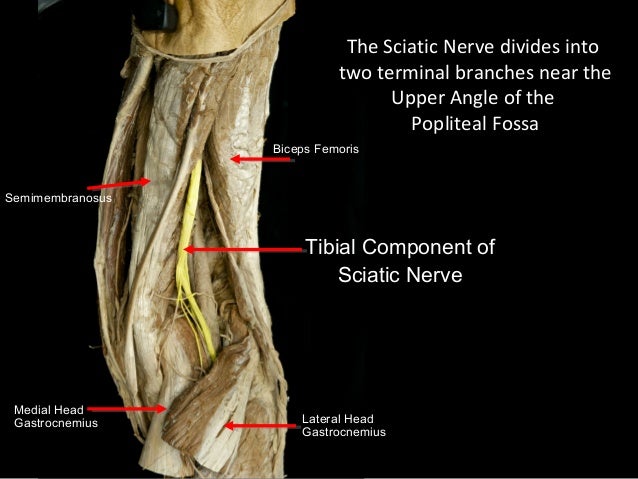



Slideshow Popliteal Fossa



Http Www Kgmu Org Digital Lectures Medical Anatomy Lecture On Popliteal Fossa Pdf
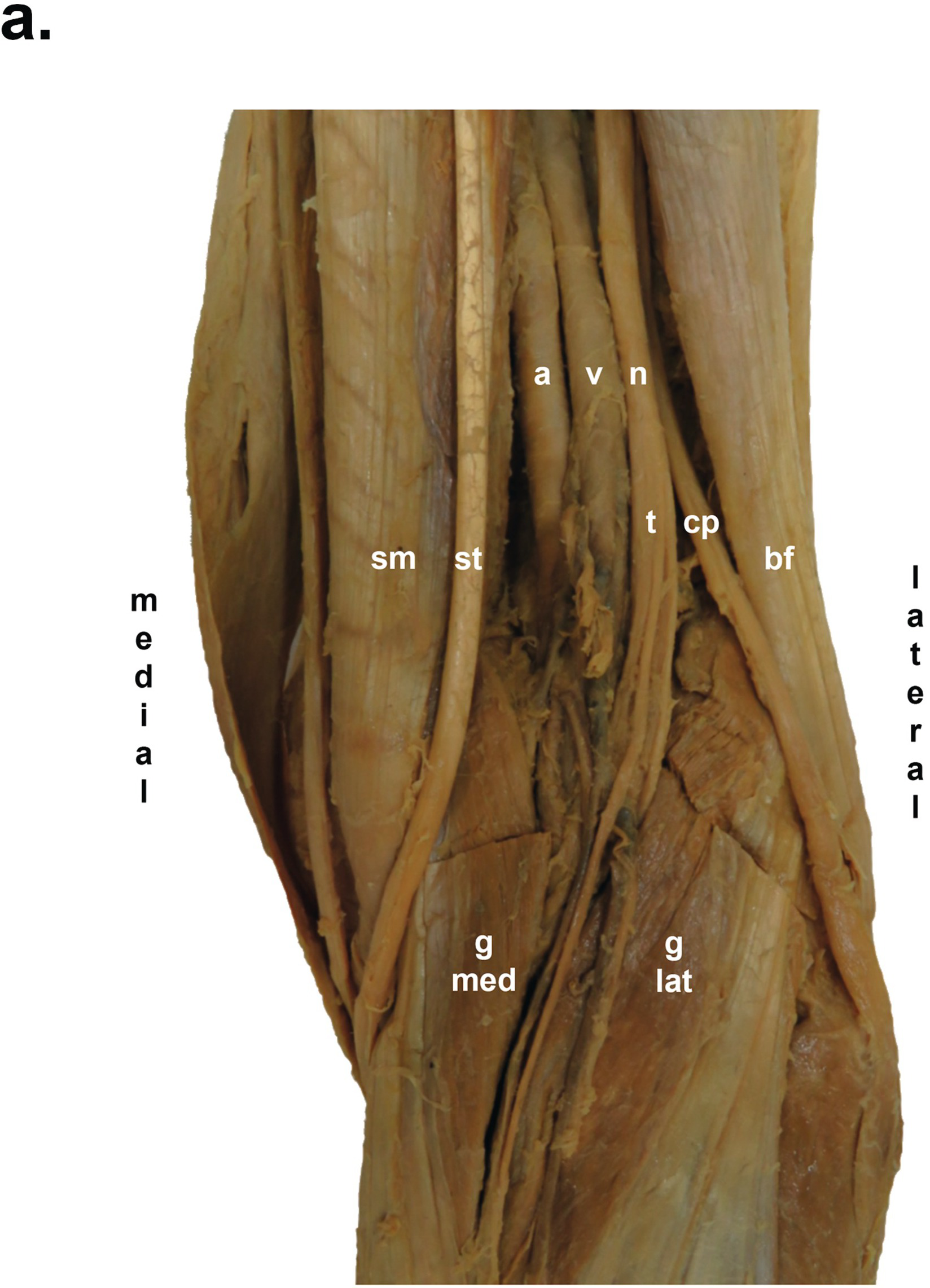
Three cutaneous nerves Branches and the terminal part of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh;Firstly, Popliteal Secondly, Popliteal vein Finally, Tibial nerve Relations of the structures in the Popliteal fossa Upper part From medial to lateral side Artery, Vein, Nerve Middle partPopliteal vein in between the artery and tibial nerve tibial nerve most superficial, giving off the sural nerve which descends to pierce the roof common fibular (peroneal) nerve runs along the lateral border, giving off a communicating sural nerve which descends to pierce the roof in the lateral fossa and join the sural nerve



2 Minute Tutorial Anatomy Of The Popliteal Fossa Youtube




Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Posterior View Of The Leg
Posterior division of the medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh; The popliteal fossa is a diamondshaped space located posterior to the knee joint It allows for the passage of critical neurovascular structures These structures, from medial to lateral, are the popliteal artery, popliteal vein, tibial nerve, and common peroneal nervePopliteal Nerve Block The "popliteal nerve" is the extension of the mid sciatic nerve But this term is a bit of a misnomer Although the name does describe its anatomic placement in the popliteal fossa, the sciatic nerve has already bifurcated into its respective distal branches relative to the popliteal artery and vein



Bats Better Anaesthesia Through Sonography




Thigh Popliteal Fossa Yeditepe Anatomy Lab
The common fibular nerve follows the biceps femoris tendon, travelling along the lateral margin of the popliteal fossa The small saphenous vein pierces the popliteal fascia and passes between the two heads of gastrocnemius to empty into the popliteal vein In the popliteal fossa, the deepest structure is the popliteal arteryThe popliteal artery (Fig 551) is the continuation of the femoral, and courses through the popliteal fossa It extends from the opening in the Adductor magnus, at the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the thigh, downward and lateralward to the intercondyloid fossa of the femur, and then vertically downward to the lower border of the Popliteus, where it divides into anterior andThe sciatic nerve and great saphenous vein are also visible The skin, superficial fascia, and deep fascia have been removed over the popliteal fossa to expose the contents of the space The muscular borders of the space are intact except for a window cut into the semimembranosus muscle to allow a view of the popliteal artery and vein near the




Popliteal Fossa Pt Master Guide




Chapter 41 Popliteal Vessels Anesthesia Key
Posteriorly, deep popliteal fascia forms the roof of the popliteal fossa It is further covered by superficial fascia which contains Short saphenous vein; The popliteal vein is located posterior to the knee in the popliteal region that is a major route for venous return from the lower leg The vein forms from the combination of the anterior and posterior tibial vein at the border of the popliteal artery The vein is found in the popliteal fossa on the posterior aspect of the kneePopliteal fossa fos´ah (pl fos´sae ) ( L ) a trench or channel;




Popliteal Fossa Notes



The Popliteal Fossa Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
The popliteal vessels and tibial nerve cross the fossa vertically, one on top of the other The tibial nerve is the most superficial, followed by the popliteal vein, which is deep or anterior to the tibial nerve, and finally, the popliteal artery, which is deepest of all The vein and nerve both cross the artery posteriorlyFound between the popliteal artery (deeply) and tibial nerve (superficially) The tributaries of the popliteal vein are the deep veins of the leg the posterior and anterior tibial veins, the common fibular veins, and the small saphenous vein The small saphenous vein enters the fossa through the popliteal fascia and drains into the popliteal—The popliteal fossa contains the popliteal vessels, the tibial and the common peroneal nerves, the termination of the small saphenous vein, the lower part of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, the articular branch from the obturator nerve, a




6 Anatomy Of Popliteal Fossa




Popliteal Fossa Flashcards Quizlet
It usually causes edema and pain in the popliteal fossa The aneurysm may stretch the tibial nerve as the artery lies deep to the nerve, resulting in pain along the medial aspect of the calf, ankle or foot (area supplied by tibial nerve) A popliteal aneurysm can be distinguished from other masses by palpable pulsations Clinical anatomy The popliteal fossa is defined as the space between the skin, the femur anteriorly and the biceps femoris muscle laterally, the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles medially, and inferiorly by both heads of the gastrocnemius (Figs 301 and 302)The space is mostly filled with fat and contains in its anterolateral aspect the popliteal vessels and nervesContents of the popliteal fossa 1 Tibial nerve and its branches 2 Common peroneal nerve and its branches 3 Popliteal artery and its branches 4 Popliteal vein and its tributaries 5 Popliteal lymph nodes 6 Popliteal pad of fat 7 Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh 8 Genicular branch of the obturator nerve Tibial nerve



Popliteal Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram



Safe Zones For Pin Placement
The normal course of the tibial nerve is to descend through the middle of the popliteal fossa, posterior to the artery that it crosses from lateral to medial It exits the popliteal fossa with the artery deep to the arch of the soleus muscleWhat does the Popliteal Fossa contain from superficial to deep?It is also frequently affected by penetrating and blunt trauma involving the lower extremity Exposure of this artery is, therefore, often required in both emergent and elective vascular procedures In close proximity to the artery, within the confines of the popliteal fossa, are the tibial nerve, common peroneal nerve, and the popliteal vein
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1844/1qimxsaGtAeyhFKKAmU4Qw_bzAdvntzTh_Vena_poplitea_1.png)



Popliteal Vein Anatomy And Location Kenhub



Safe Zones For Pin Placement
Varicose veins occasionally arise from nonsaphenous tributaries 1 In some cases, these varicose veins appear in the popliteal fossa, via perforating veins At the lateral border of the popliteal fossa, the common peroneal nerve runs just beneath the deep fascia
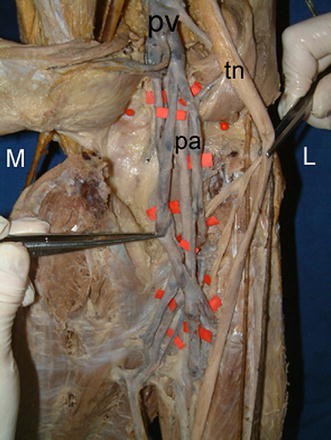



Figure 2 Anatomic Variations Of Popliteal Artery That May Be A Reason For Entrapment Springerlink




The Popliteal Fossa Human Anatomy



Www Kgmu Org Digital Lectures Medical Anatomy Dr Kaveri Anatomy Lecture On Popliteal Fossa Pdf



Popliteal Fossa Boundaries Contents Anatomy Tutorial Youtube




Popliteal Fossa Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Popliteal Fossa Physiopedia




Popliteal Fossa And Knee Joint Last S Anatomy Regional And Applied




Anatomy Of The Left Popliteal Fossa Download Scientific Diagram




Vascular Problems Of The Knee Musculoskeletal Key



Uomustansiriyah Edu Iq Media Lectures 2 2 19 03 31 01 18 32 Pm Pdf




The Popliteal Artery Human Anatomy




3d Printed Popliteal Fossa Distal Thigh And Proximal Leg




Popliteal Fossa Diagram Quizlet
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/popliteal-artery/4fcNkYGQccOl0OkvY8cuw_gA4gQRyxVpboWSaGf9cUxw_A._poplitea_m01.png)



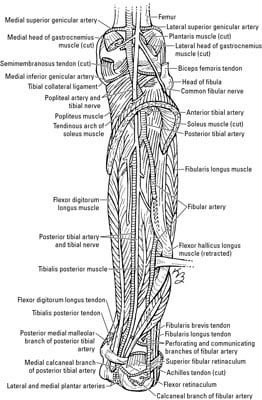
Popliteal Artery Anatomy Branches Location And Course Kenhub




Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora



Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block Anesthesia Key



Popliteal Fossa




How To Perform Ultrasound Guided Distal Sciatic Nerve Block In The Popliteal Fossa Acep Now



Safe Zones For Pin Placement




Popliteal Fossa Its Boundaries Contents And Clinical Correlates Kyrmed




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Back Of Thigh And Popliteal Fossa Myhumananatomy




01x Normal Anatomy Of The Right Knee And Popliteal Fossa Anatomy Exhibits



Surgical Exposure Of The Lower Extremity Arteries Thoracic Key



Www Medicinebau Com Uploads 7 9 0 4 Publiteal Fossa Pdf




Popliteal Artery Wikipedia




Part Five Popliteal Fossa And Knee Joint




Popliteal Fossa Block Regional Anesthesia Mitch Medical Healthcare




Anatomy Of The Popliteal Fossa Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube




Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora



Ksumsc Com Download Center Archive 1st 438 2 musculoskeletal block Team work Anatomy Lecture 2816 29 popliteal fossa Pdf




Popliteal Fossa World Wide Lifestyles Weight Loss And Gain Tips



Popliteal Fossa Boundaries Contents And Applied Aspects Anatomy Qa



Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymphatics Of The Knee And Leg Dummies




Korean Journal Of Anesthesiology




Popliteal Fossa And Block Saq 11 Anatomy For The Frca




Knee Pit Nerve Supply Muscle Attachment Functions Rxharun




Ultrasound Guided Popliteal Block Wfsa Resources
/GettyImages-87313663-16bdfeaf37d048dbaef06b4f00b269b5.jpg)



Popliteal Vein Anatomy And Function



Uomustansiriyah Edu Iq Media Lectures 2 2 19 03 31 01 18 32 Pm Pdf



1



Cambridge Orthopaedics Popliteal Block Uk




Anterior Posterior Medial Fascial Compartments Of The Thigh Ppt Download




Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Wikipedia



Right Popliteal Vein Aneurysm A Case Report




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Popliteal Artery Wikipedia




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Popliteal Artery Anatomy Branches Location And Course Kenhub



Easy Notes On Popliteal Fossa Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
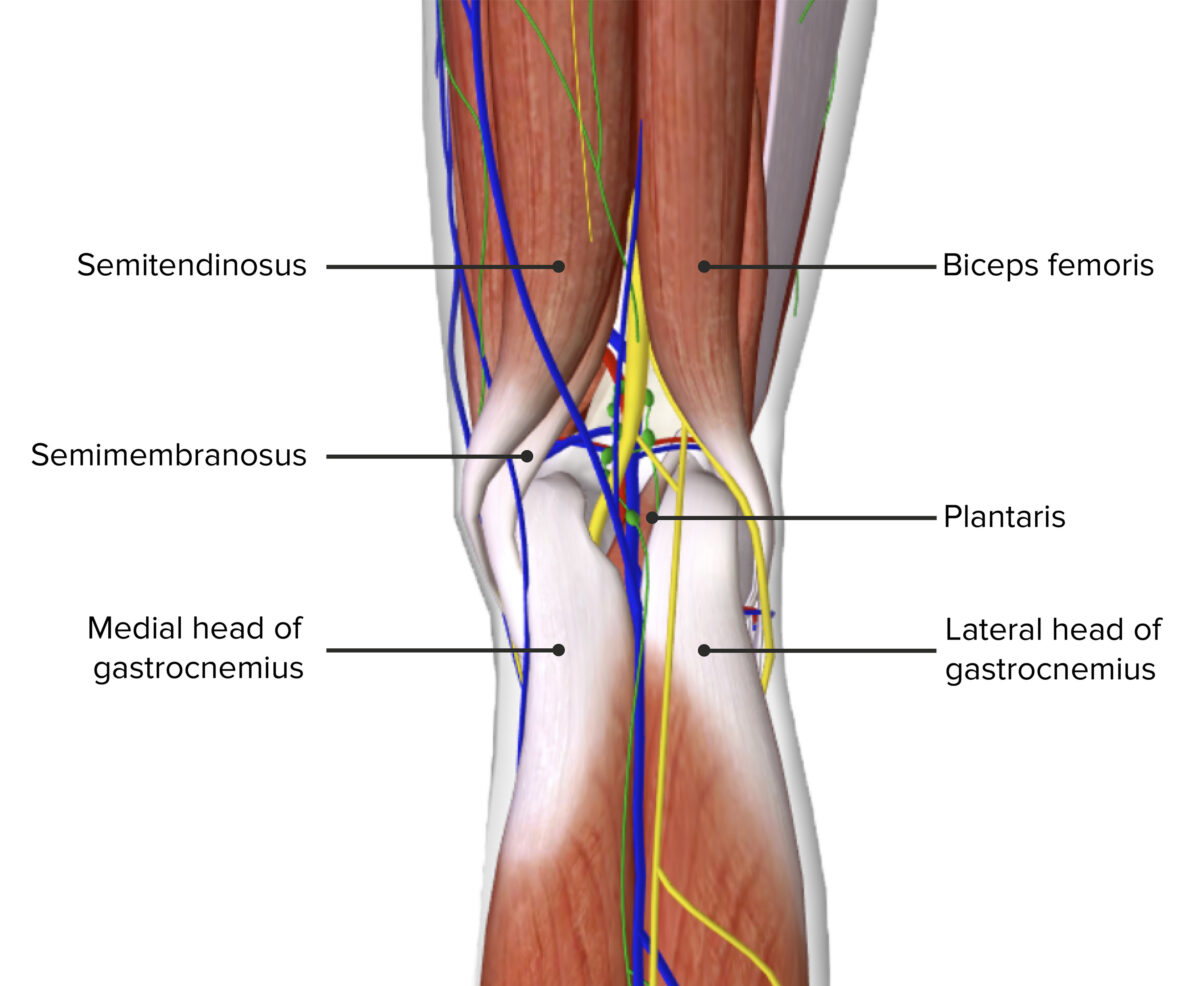



Popliteal Fossa Concise Medical Knowledge




Poplitealfossa Explore Facebook




Anatomy Of The Popliteal Fossa Osmosis




Popliteal Nerve Block Is A Block Of The Sciatic Nerve In The Popliteal Fossa The Block Provides Anesthesia For Surgery On Nerve Anatomy Sciatic Nerve Anatomy
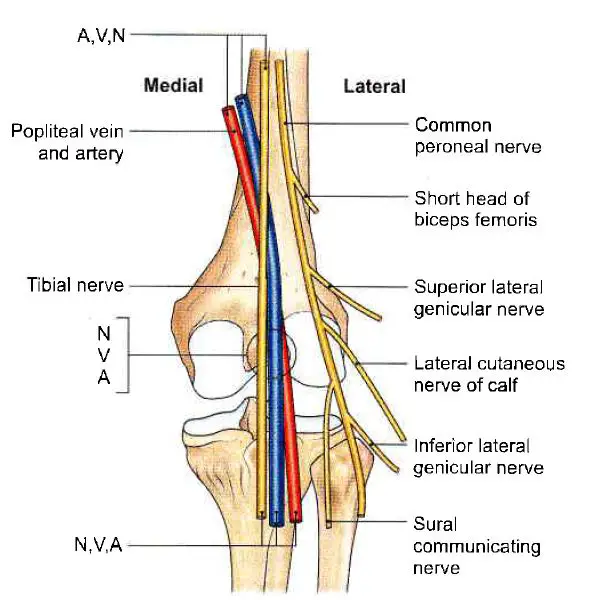



Popliteal Fossa Complete Anatomical Overview Learn From Doctor




Compression Syndromes Of The Popliteal Neurovascular Bundle Due To Baker Cyst Sciencedirect




Popliteal Entrapment Syndrome A Report Of Tibial Nerve Entrapment Journal Of Vascular Surgery




The Popliteal Fossa Boundaries Contents Youtube



Anatomy And Contents Of The Popliteal Fossa Orthopaedicprinciples Com



Popliteal Artery Entrapment A Mysterious Syndrome



1



Q Tbn And9gcsgzf2avhrramdooe0ztrie4bkshn5uham3xqnv2ajk9u0xpfhe Usqp Cau




The Popliteal Fossa Fig 178 Clinical Features Click To Cure Cancer
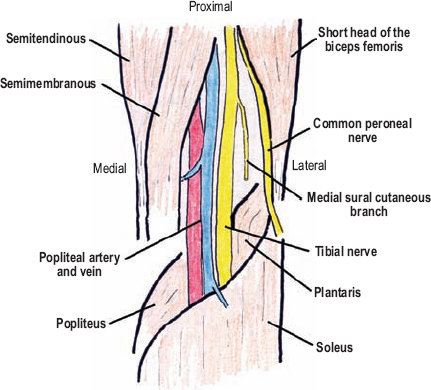



The Diagnostic Anatomy Of The Sciatic Nerve Neupsy Key
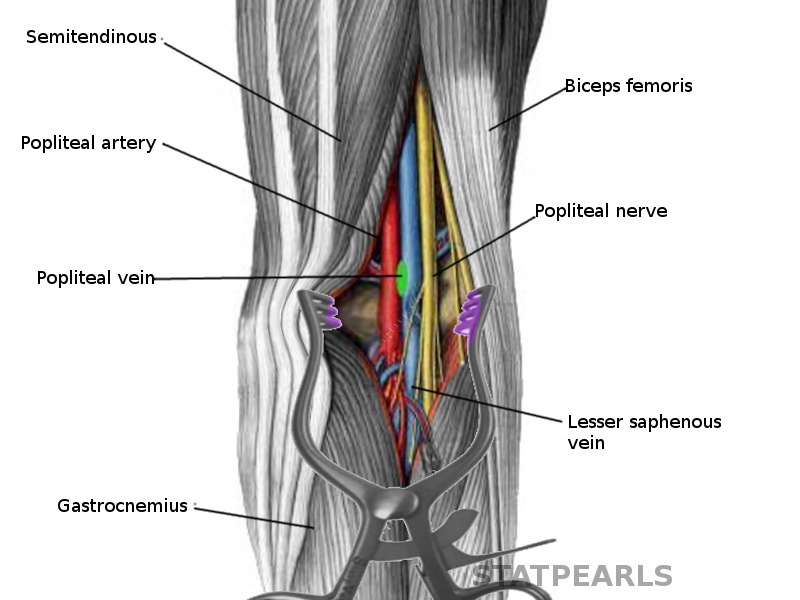



Figure Popliteal Fossa Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Humannervesspinalfoot Ahuman Human Spinal Lumbosacral Nerves Foot And Lower Leg Create The Personality Nerve Anatomy Sciatic Nerve Anatomy




The Knee Joint Classification Of The Joint Modified




Popliteal Fossa Nerve Supply Muscle Attachment Functions Rxharun
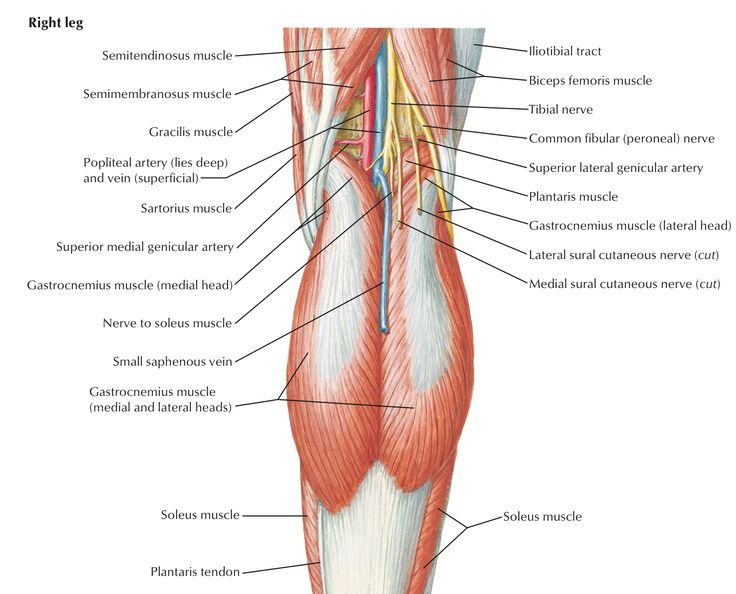



Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Contents Bone And Spine
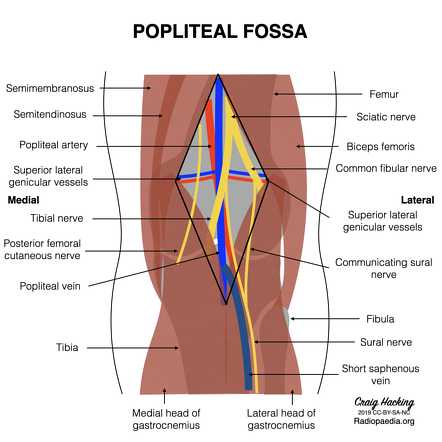



Popliteal Fossa Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
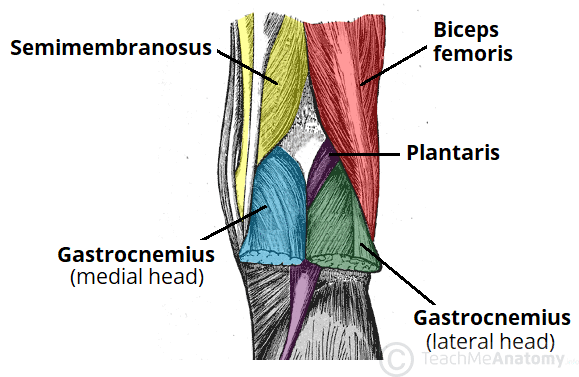



The Popliteal Fossa Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy




3 10 Popliteal Fossa And Leg Flashcards Quizlet




Test Popliteal Fossa Quizlet




Anatomy Of Popliteal Fossa Anatomy Drawing Diagram



Http Www Kgmu Org Digital Lectures Medical Anatomy Lecture On Popliteal Fossa Pdf




Popliteal Fossa Physiopedia
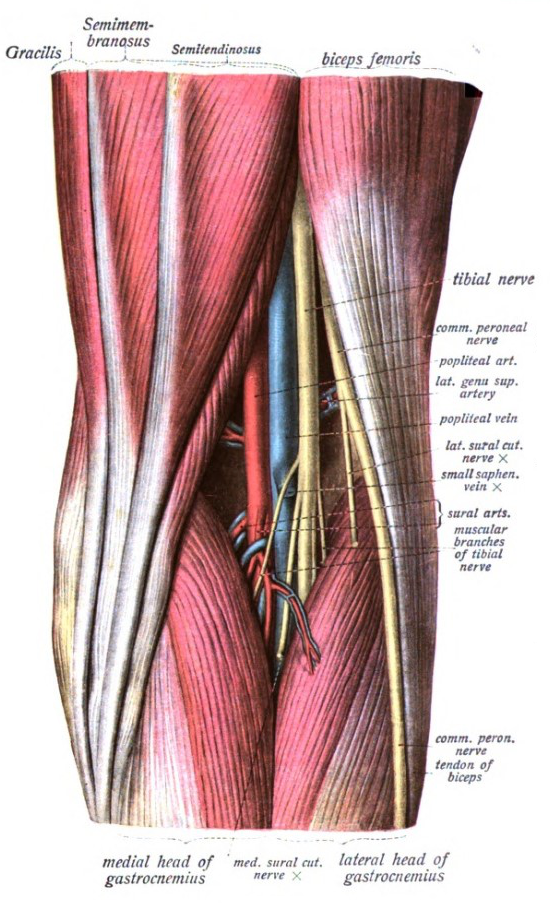



Popliteal Fossa Wikipedia



Popliteal Fossa Concise Medical Knowledge




Popliteal Fossa Bf Biceps Femoris Pa Popliteal Artery Pv Download Scientific Diagram




Thigh Knee And Popliteal Fossa Knowledge Amboss



No comments:
Post a Comment